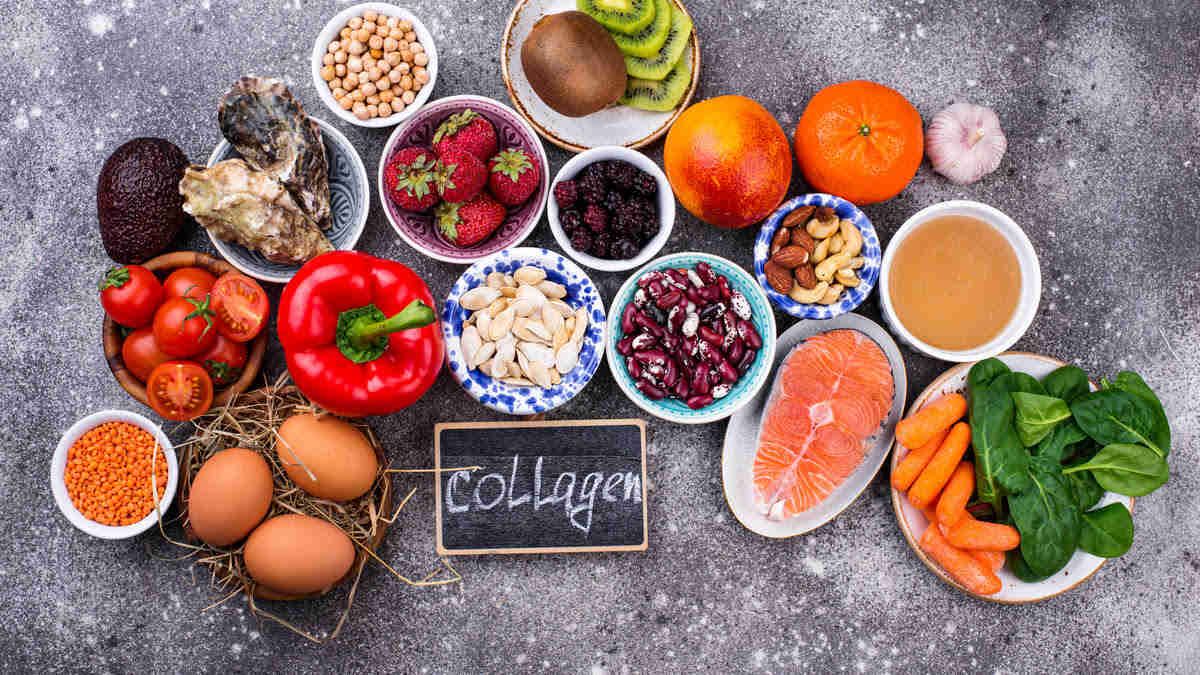
Collagen and gelatin are two proteins that are steadily gaining popularity as support for joint, bone and skin health. While they may appear similar at first glance, they differ in both their properties and possible applications. Gelatin is widely used in the food industry, while collagen dominates in the form of dietary supplements, promising to improve skin elasticity and the condition of the musculoskeletal system. So when is it worth reaching for collagen and when for gelatin? How do these substances affect our bodies? In this article, we’ll look at their key differences to help consumers make a conscious choice.
What is collagen?
Collagen is an essential structural protein that plays a key role in maintaining the integrity and elasticity of tissues in the body. It accounts for as much as one-third of the total weight of proteins in our body, and its unique structure – a triple polypeptide chain – provides high tensile strength and stability. The structure of collagen is dominated by amino acids such as glycine, proline, hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine, which contributes to its unique properties.
The human body contains as many as 29 types of collagen, the most important of which are:
- Type I – most commonly found in bones, skin, tendons and ligaments, provides them with strength and flexibility.
- Type II – the main component of vitreous cartilage, supports joint cushioning.
- Type III – found in the skin and internal organs, where it is responsible for their elasticity.
- Type V – present in the skin, bones and cornea, has a supportive function for tissue structure.
- Type XI – can be found in cartilage and intervertebral discs, where it provides adequate cushioning.
Collagen is a common ingredient in supplements that support joint health and skin care products. Products containing hydrolyzed collagen are distinguished by their better assimilability, which increases their effectiveness and brings faster noticeable results.
Do we absorb collagen from food?
The question of the bioavailability of collagen from the diet is causing much controversy, but scientific research indicates that it is possible. Natural products such as jellies, offal, shanks or cooked cartilage contain collagen proteins, which the body is able to utilize to some extent – it is estimated that we can absorb about 8-10% of collagen from such foods.
However, the greatest benefit of collagen absorption comes from dietary supplements that contain collagen in hydrolyzed form, in which the protein has been broken down into smaller molecules, such as peptides and free amino acids. This allows the body to assimilate it much more efficiently than collagen in its natural form. Interestingly, to further support the production of this protein, it is worth enriching the diet with products containing vitamin C, zinc and copper, which stimulate the synthesis of new collagen fibers.
Collagen vs gelatin
Collagen is a key structural protein that plays an invaluable role in maintaining the elasticity and strength of the body’s tissues. Gelatin, on the other hand, is a product formed from partially decomposed collagen, containing an almost identical amino acid composition. The differences between these substances are mainly due to their structure and chemical properties, which affect how they are used and absorbed.
Differences in structure and absorption
Collagen and gelatin have similar amino acid composition, but their molecular structures differ significantly. Collagen supplements are characterized by smaller molecules, which makes them easier for the body to absorb, so they are used more quickly to support skin, joints and bones. Gelatin, due to its larger molecules, is absorbed somewhat more slowly, making it more readily used in culinary applications than as a health supplement.
Collagen in supplements, gelatin in the kitchen
Collagen is popular mainly in dietary supplements, where it is used to support skin, hair, nail and joint health. Gelatin, on the other hand, as a thickening and stabilizing product, is widely used in the food industry – from desserts to processed meat products.
Dissolution properties
Another important difference is its dissolving properties. Collagen, especially in its hydrolyzed form, dissolves in both hot and cold water, making it easy to add to a variety of beverages and foods. Gelatin, on the other hand, requires hot water to dissolve completely, and forms a thick gel when cooled, which is an advantage in a culinary context, but limits its use as a dietary supplement.
Are gelatin and collagen the same thing?
Although the names “collagen” and “gelatin” are sometimes used interchangeably, the two substances differ in structure and properties. Gelatin is a form of collagen that has been partially hydrolyzed, which allows it to be used in various culinary and cosmetic applications. However, gelatin is not the same as collagen available in dietary supplements – it differs not only in molecular structure, but also in the degree of absorption.
Collagen in the form of supplements is usually found in hydrolyzed form, meaning that its molecules are fragmented, which increases its bioavailability and facilitates its absorption by the body. Gelatin, while also containing collagen, is less effective for health supplementation, as the body absorbs it more slowly and less efficiently.
How much collagen is in gelatin?
Gelatin is a product with a high collagen content of up to 90%. It mainly consists of type I collagen, which plays a key role in maintaining the health of skin, hair and nails. Dietary supplements often use hydrolyzed collagen, containing not only type I, but also type II, which is present in joint cartilage to promote its flexibility and regeneration. Type III collagen, which interacts with type I, is also present in some supplements, enhancing their beneficial effects on the body.
Properties of collagen and gelatin
Collagen and gelatin, thanks to their common amino acid profile, exhibit similar health properties, supporting various aspects of the body’s function. Both collagen supplementation and regular consumption of gelatin can have positive effects on joint, skin and digestive health. Here are the most important benefits of their use:
Joint and musculoskeletal support
- Reduction of joint pain – both collagen and gelatin promote cartilage regeneration, which helps reduce joint-related pain.
- Prevention of musculoskeletal disorders – regular intake of these proteins can delay the development of joint and bone-related ailments, such as osteoporosis.
Tissue regeneration and bone structure
- Rebuilding damaged tissues – collagen and gelatin promote regeneration after injury, contributing to faster wound healing and improved tissue structure.
- Bone strengthening – affect bone density, promoting bone stability and strength, which is important in fracture prevention.
Effects on skin, hair and nails
- Improving skin elasticity – collagen and gelatin affect skin firmness and elasticity, helping to smooth wrinkles and improve hydration.
- Reducing hair loss and strengthening nails – the use of these proteins strengthens hair structure, reduces hair breakage and promotes nail growth.
Health of the digestive system
- Supporting intestinal health – gelatin and collagen strengthen the intestinal barrier, which can contribute to better digestive function and reduce the risk of intestinal discomfort.
With these properties, both collagen and gelatin can support the body in many areas, benefiting our health and appearance.
Collagen or gelatin?
The decision between collagen and gelatin depends mainly on your individual needs and purpose of use. Both products can support joint, skin and digestive health, but their specific properties make them different in effectiveness and application.
Gelatin – for culinary and health support
Gelatin is an excellent choice if you want to enrich the texture of food or prepare a dessert with a creamy texture. Available in almost every grocery store, it is also an economical option that supports skin, bone and joint health. Gelatin, despite its slightly slower absorption, provides the body with essential amino acids, so it benefits the regeneration and strength of connective tissue.
Collagen – for better absorption and health benefits
Collagen supplements, especially those in hydrolyzed form, are characterized by a smaller molecule, which increases their bioavailability and effectiveness. Collagen is more recommended for those seeking intensive health support for joints, skin and hair. Due to faster and more efficient absorption, collagen supplementation is ideal for those struggling with musculoskeletal diseases or looking for effective ways to slow down the aging process.
When to take collagen and when to take gelatin?
- Gelatin is ideal for enriching foods and as a less expensive alternative to support everyday health.
- Collagen will work well as an intensive supplement for those in need of deeper regenerative support or anti-aging prevention.
Regardless of your choice, both substances have valuable health benefits to offer, so be sure to tailor them to your needs to reap their full benefits.
Gelatin vs collagen | Summary
Although gelatin and collagen come from the same source and have similar amino acid composition, they differ in structure, absorption and use. Collagen, available in dietary supplements, is easily absorbed due to its hydrolyzed form, making it effective in supporting skin, joint and bone health. Gelatin, on the other hand, commonly used in cooking as a thickening agent, provides valuable amino acids, although the body absorbs it less efficiently than collagen in hydrolyzed form.
The choice between gelatin and collagen should depend on your needs. If your goal is intensive health support and tissue regeneration, collagen in supplement form will be the best option. Gelatin, on the other hand, will work well as a healthy dietary supplement that can benefit the appearance of your skin and strengthen the structure of your hair and nails. Both forms have their own unique properties, which are worth taking advantage of to improve health and quality of life.